Low-E, or low emissivity, glass is a revolutionary innovation in the world of architecture and construction. It has gained popularity for its ability to improve energy efficiency, enhance indoor comfort, and contribute to sustainable building practices. In this article, we will explore what Low-E glass is, how it works, and its significance in modern construction.
Understanding Low-E Glass
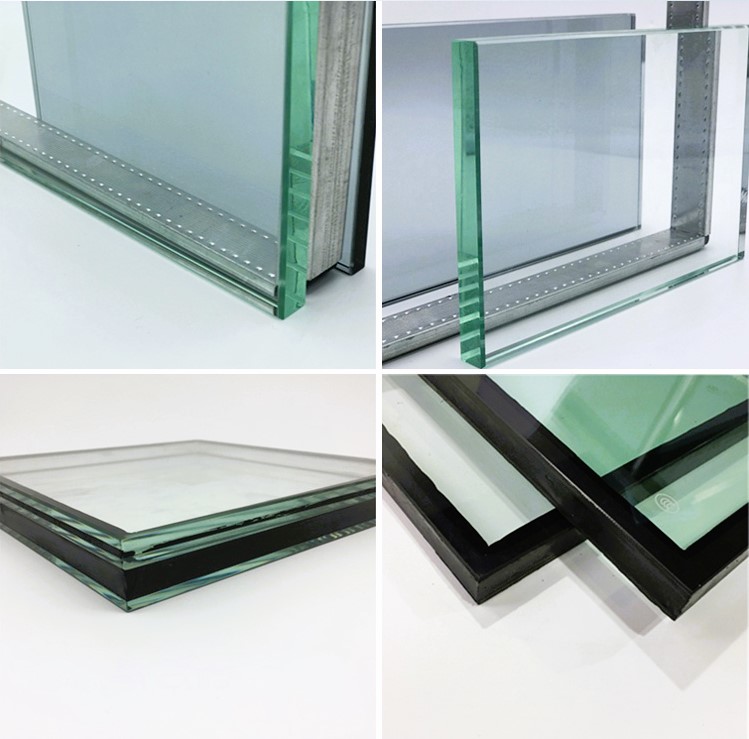
Low-E glass is a type of coated glass that has a microscopically thin, transparent layer of special metallic material applied to its surface. The term “low emissivity” refers to the glass’s ability to emit (radiate) low levels of thermal energy (heat) when compared to other types of glass.
The concept behind Low-E glass is to control the transmission of heat and solar energy through windows while maintaining visibility and allowing natural light to enter a building. It achieves this through the use of a thin, virtually invisible coating that reflects and absorbs certain wavelengths of light and heat.
How Does Low-E Glass Work?

Low-E glass works on the principle of selective reflection and absorption of electromagnetic radiation. It has several key properties and mechanisms that contribute to its effectiveness:
1. Reflectivity: The Low-E coating is designed to reflect a significant portion of infrared (IR) radiation, which carries heat. This reflective property helps keep heat from escaping the interior of a building in cold weather and prevents outdoor heat from entering in hot weather.
2. Absorption: Low-E glass also absorbs a portion of the incoming solar radiation, particularly in the ultraviolet (UV) and near-infrared (NIR) spectrum. This helps reduce the amount of heat that penetrates through the glass while allowing visible light to pass through.
3. Transparency: The coating is highly transparent to visible light, ensuring that natural light enters the building, maintaining visual clarity, and minimizing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
4. Emissivity: Low-E glass has low emissivity, meaning it emits only minimal amounts of heat radiation from its surface. This property helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature and prevents heat loss during the colder months.
5. Dual-Surface Coating: Some Low-E glass products feature a dual-surface coating, with one coating on the inner surface (facing the interior of the building) and another on the outer surface (facing the exterior). This dual-coating design maximizes energy efficiency by addressing both heat gain and heat loss.
Significance in Modern Construction
Low-E glass has become a key component in sustainable and energy-efficient building design for several reasons:
1. Improved Energy Efficiency: By reducing heat transfer through windows, Low-E glass helps lower heating and cooling costs. It allows buildings to maintain comfortable temperatures year-round with reduced reliance on HVAC systems.
2. Enhanced Comfort: Low-E glass minimizes temperature variations near windows, eliminating cold drafts in winter and reducing heat gain in summer. This creates a more comfortable indoor environment.
3. UV Protection: Low-E coatings block a significant portion of harmful UV rays that can cause fading and damage to interior furnishings, flooring, and artwork. This protects occupants and investments in the building.
4. Sustainability: Low-E glass contributes to sustainable building practices by reducing energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and a building’s overall carbon footprint.
5. Compliance with Building Codes: In many regions, building codes and energy efficiency standards now require the use of energy-efficient materials like Low-E glass in new construction and renovation projects.
6. Daylighting: Low-E glass maximizes the benefits of daylighting, which is the use of natural light to illuminate interior spaces. This reduces the need for artificial lighting during the day, saving energy and reducing electricity costs.
Conclusion: A Clear Choice for Energy Efficiency
Low-E glass has revolutionized the way we think about windows and glazing in buildings. Its ability to control heat transfer while maintaining visibility and natural light makes it a clear choice for energy-conscious construction. As sustainable building practices continue to gain importance, Low-E glass will play a pivotal role in creating comfortable, eco-friendly, and energy-efficient spaces for generations to come.
For more information on Low-E glass and its applications in construction, you can visit Canada.ca. These standards ensure the quality and performance of Low-E glass products used in Canadian buildings.