The role of glass in modern vehicles extends far beyond providing a clear view of the road ahead. Today’s automotive glass is engineered to enhance safety, protect occupants, and improve the overall driving experience. In this article, we will explore the importance of protective glass in vehicles, the technologies behind it, and how it contributes to vehicle safety and comfort.
The Evolution of Automotive Glass
Automotive glass has come a long way since the early days of the automobile. In the past, simple flat glass windshields offered minimal protection from the elements and road hazards. However, as the automotive industry evolved, so did the need for more advanced glass solutions.
Importance of Protective Glass
Protective glass in vehicles serves several crucial functions:
- Safety: Perhaps the most critical role of automotive glass is to protect vehicle occupants. It prevents passengers from being ejected during accidents and shields them from flying debris and harsh weather conditions.
- Visibility: Clear and undistorted visibility is essential for safe driving. Protective glass ensures that drivers have an unobstructed view of the road, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Security: Automotive glass is designed to deter theft and vandalism. Laminated glass, for example, is difficult to shatter, making it harder for thieves to break into vehicles.
- Comfort: Protective glass also contributes to passenger comfort by reducing noise and blocking harmful UV rays. It helps maintain a stable and comfortable interior environment.
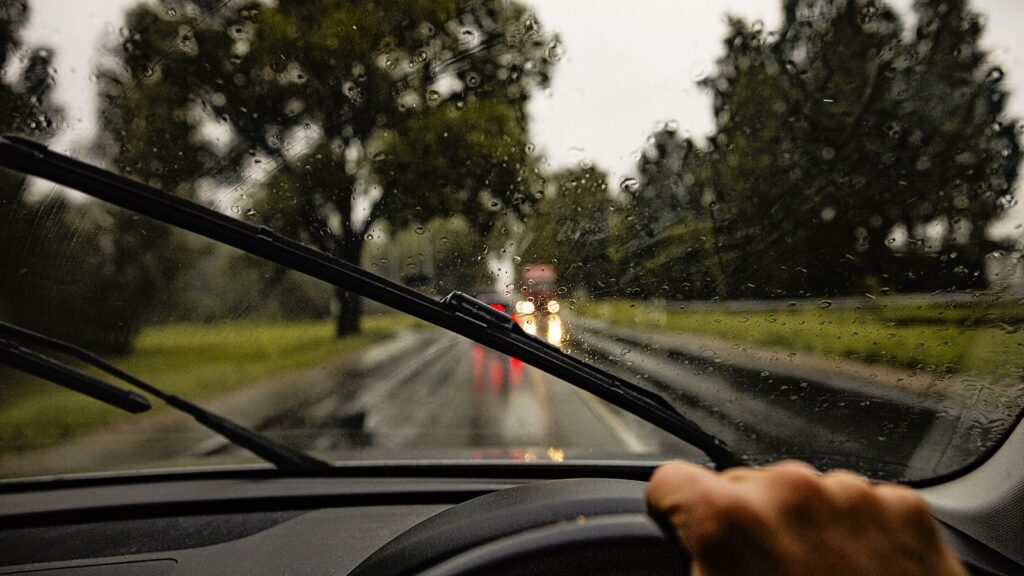

Types of Protective Glass
Several types of glass are used in modern vehicles to provide protection and functionality:
- Tempered Glass: Tempered glass is used for side and rear windows. It is designed to shatter into small, dull-edged pieces when broken, reducing the risk of injury to occupants.
- Laminated Glass: Laminated glass is commonly used for windshields. It consists of layers of glass and a plastic interlayer that holds the glass together when shattered, preventing it from shattering into pieces. This enhances safety and prevents ejection during accidents.
- Solar-Control Glass: Solar-control glass has a special coating that reduces the transmission of heat and UV rays into the vehicle. It helps keep the interior cooler and protects passengers from harmful UV radiation.
- Sound-Reducing Glass: Sound-reducing or acoustic glass is designed to reduce exterior noise, creating a quieter and more comfortable cabin environment. Glass in the space industry, read more at the link.
Advanced Technologies in Protective Glass
Innovations in automotive glass technology have led to the development of advanced features and capabilities:
- Heads-Up Displays (HUDs): Some vehicles feature HUDs that project essential information, such as speed and navigation directions, onto the windshield. This allows drivers to access critical information without taking their eyes off the road.
- Rain-Sensing Wipers: Rain-sensing technology uses sensors on the windshield to detect rain or moisture and automatically activate windshield wipers, improving visibility during wet conditions.
- Infrared Reflective Coatings: Infrared-reflective coatings on glass help block heat and UV rays, enhancing comfort and reducing the need for excessive air conditioning.
- Self-Healing Glass: Researchers are developing self-healing glass that can repair minor scratches and chips automatically, reducing the need for costly replacements.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): ADAS technologies, including sensors and cameras integrated into the glass, enable features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and collision avoidance.
Standards and Regulations
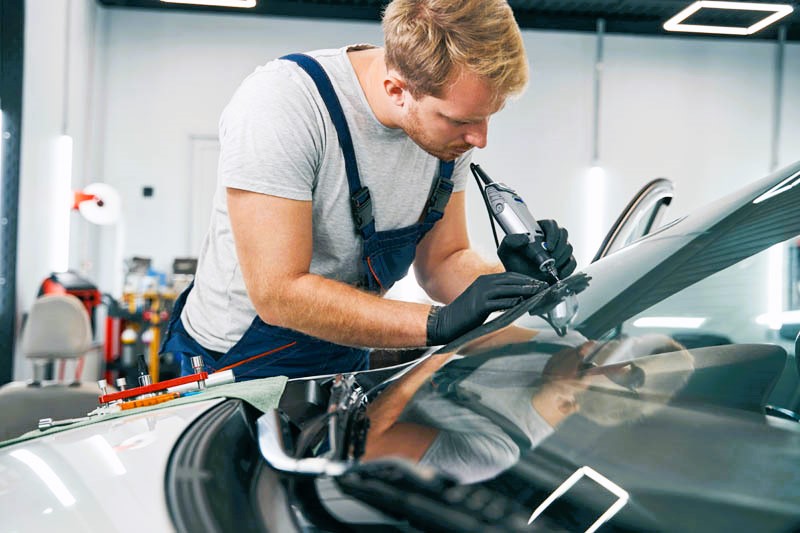

The automotive industry adheres to stringent standards and regulations regarding protective glass to ensure safety and performance. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and government agencies like Transport Canada set standards and guidelines for automotive glass quality, durability, and safety.
For example, ISO 3538 specifies safety glazing materials for road vehicles, including requirements for laminated and tempered glass used in windshields and windows. These standards help manufacturers produce glass products that meet safety and performance criteria.
Conclusion
Protective glass in vehicles is a critical component of automotive safety and comfort. Its evolution from simple flat glass to advanced laminated, tempered, and specialized glass technologies has significantly improved vehicle safety and the driving experience. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovations in automotive glass, further enhancing protection and convenience for vehicle occupants.
For more detailed information on protective glass for vehicles, you can visit Wikipedia. These sources provide valuable insights into the technical aspects and industry standards associated with protective glass in vehicles.